Endocannabinoid System
Updated September 11, 2024
What Is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system found in the bodies of all mammals. It plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, or balance, within the body by regulating a variety of physiological processes. The ECS consists of three primary components: endocannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors, and metabolic enzymes.
Endocannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds produced by the body that bind to cannabinoid receptors, which are located throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems. There are two primary types of receptors involved: CB1 receptors (primarily found in the brain and central nervous system) and CB2 receptors (mainly located in the immune system and peripheral tissues).
When endocannabinoids bind to these receptors, they initiate various responses that help manage pain, mood, appetite, memory, and immune response, among other functions. After the endocannabinoids have fulfilled their purpose, metabolic enzymes break them down to ensure the body maintains homeostasis.
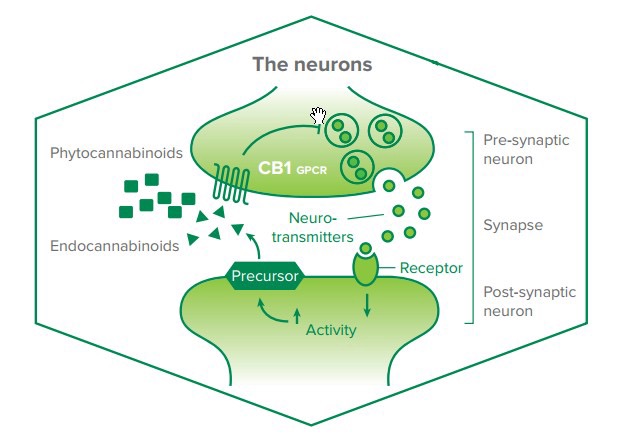
What Are the Functions of the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis throughout the body by regulating a variety of physiological processes. Its primary functions include:
- Mood Regulation: The ECS helps balance emotions and manage stress to generate feelings of happiness and wellbeing.
- Pain Management: The ECS plays a significant role in modulating pain perception and can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Appetite Control: The ECS is involved in regulating hunger and the body's energy balance, thereby influencing eating habits and food intake.
- Immune Response: The ECS modulates the body's immune system to maintain healthy immune function and regulate inflammatory responses.
- Sleep Regulation: The ECS contributes to the regulation of sleep patterns to foster healthy rest and recovery.
- Memory and Learning: The ECS influences cognitive functions, thereby impacting memory formation and learning processes.
When Was the Endocannabinoid System Discovered?
The endocannabinoid system was discovered in the early 1990s by researchers who were investigating the effects of cannabinoids, particularly THC. In 1992, Raphael Mechoulam and his team identified the first endocannabinoid, anandamide, which is a naturally occurring compound in the body that binds to cannabinoid receptors.
This discovery paved the way for further research into the ECS, uncovering its crucial role in regulating a variety of physiological processes, including pain, mood, appetite, and memory. Over the following years, researchers identified additional endocannabinoids and receptors, expanding our understanding of this complex system and its therapeutic applications.
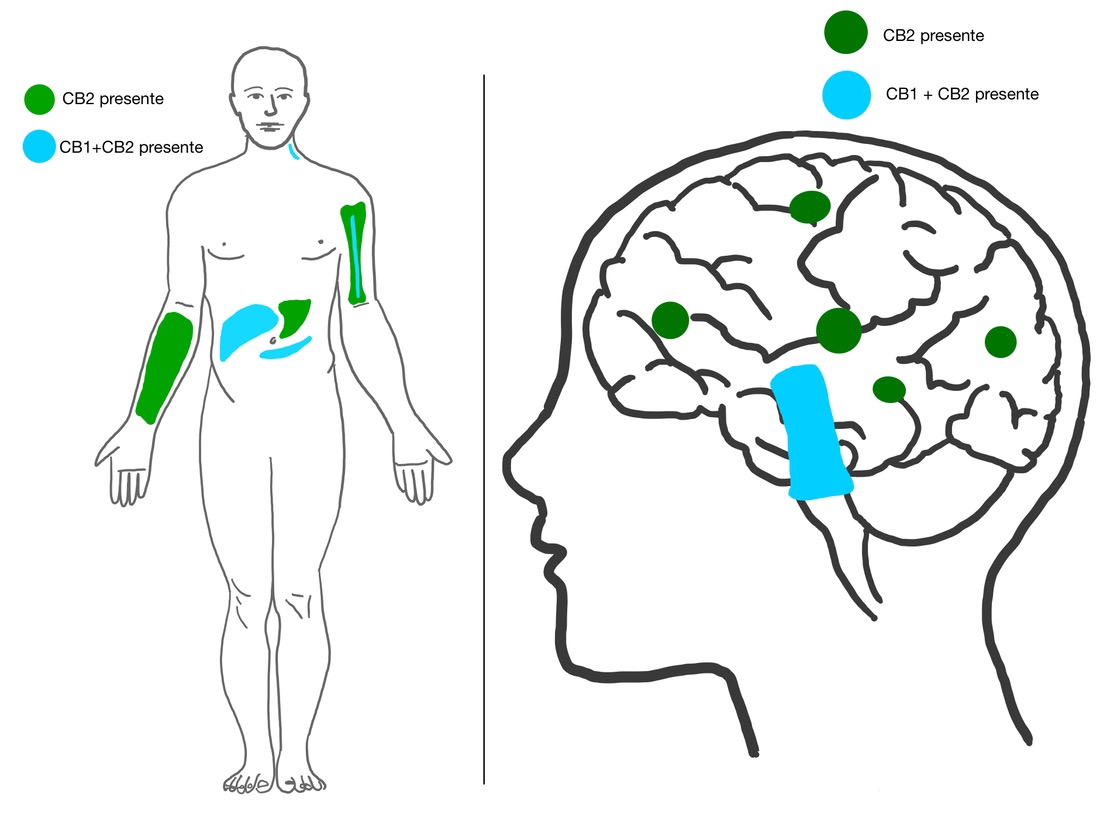
How Does THC Interact with the ECS?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive compound in medical marijuana, interacts with the endocannabinoid system by binding to cannabinoid receptors (primarily CB1 and CB2). When THC binds to CB1 receptors, it can produce psychoactive effects, leading to the sensation of being "high." This interaction can also influence emotional response and memory.
THC's binding to CB2 receptors can modulate inflammation and pain response, contributing to its therapeutic effects. By engaging with these receptors, THC can significantly alter the body's homeostasis and provide medical benefits such as pain reduction and appetite stimulation.
How Does CBD Interact with the ECS?
When CBD, or cannabidiol, interacts with the endocannabinoid system, it does not bind directly to the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors like THC. Instead, CBD is thought to influence the ECS by elevating the levels of endocannabinoids naturally produced by the body--particularly anandamide, which plays a role in regulating mood, pain sensation, and memory.
This interaction may help promote homeostasis within the body, offering therapeutic effects such as anxiety reduction and pain relief.
What Are the Symptoms of Endocannabinoid Deficiency?
Endocannabinoid deficiency is a condition characterized by inadequate production of endocannabinoids or ECS dysfunction. This deficiency can disrupt various physiological processes and is thought to contribute to many health issues related to mood, pain, appetite regulation, and more.
The symptoms of endocannabinoid deficiency include:
- Increased anxiety and depression
- Chronic pain or heightened sensitivity to pain
- Persistent inflammation
- Difficulty sleeping or insomnia
- Reduced appetite or overeating
- Problems with memory and cognitive function
- Unexplained fatigue or lack of energy
- Digestive issues such as nausea or irritable bowel syndrome
- Skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or acne
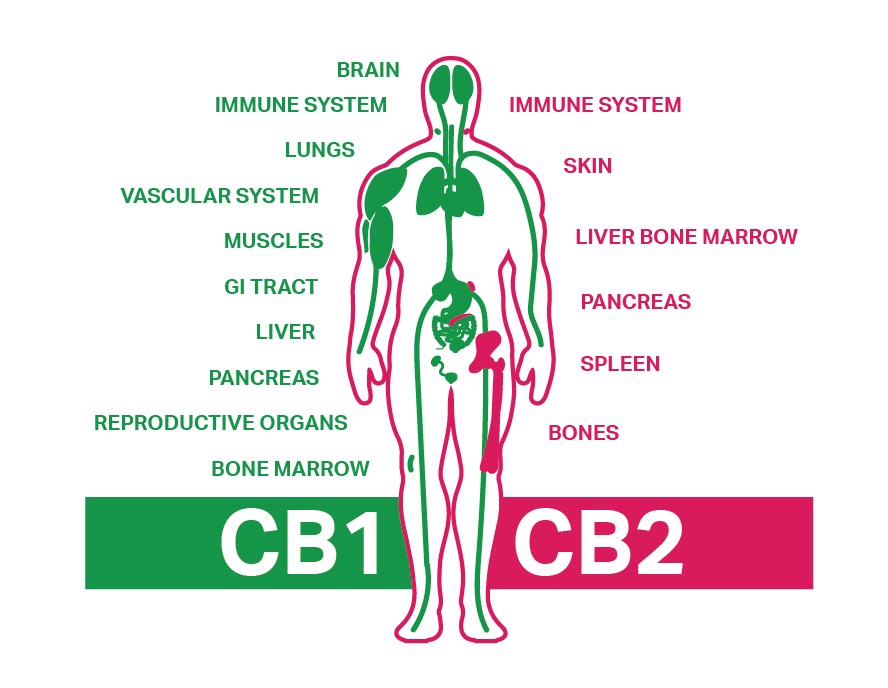
How Can You Support Your Endocannabinoid System?
Supporting your endocannabinoid system can improve its function and promote overall well-being. Here are some effective ways to do so:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Incorporate omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. These are crucial to the functioning of the ECS.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in routine physical activity to boost your endocannabinoid levels naturally, improve your mood, and reduce stress.
- Manage Stress: Practice mindfulness techniques like meditation or yoga to help regulate stress and promote ECS balance.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Follow a consistent sleep schedule. Quality sleep is vital for ECS regulation and overall health.
- Consider Natural Supplements: Explore CBD or other cannabinoid-rich supplements to support the functioning of your ECS.
- Hydrate: Dehydration can hinder ECS performance, so drink plenty of water each day.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt the ECS's balance and cause dysfunction, so limit your alcohol intake.
- Avoid Harmful Substances: Stay away from tobacco and limit your caffeine intake, as these substances can interfere with ECS regulation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, everyone has an ECS. This complex cell-signaling system exists in all mammals. While individual ECS activity can vary based on genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors, the presence of this system is universal.
The endocannabinoid system has been identified in a wide variety of species, including mammals such as dogs, cats, horses, and primates. Additionally, research suggests that the ECS may exist in other vertebrates, like birds, fish, and reptiles.
The release of endocannabinoids can be triggered by various physiological stimuli. Physical activity is a significant trigger, as exercise leads to an increase in endocannabinoid levels. Stress responses, including acute stress from trauma or anxiety, can also cause the release of endocannabinoids.
Additionally, certain foods--particularly those rich in omega-3 fatty acids--may encourage endocannabinoid production.
Endocannabinoid deficiency can be attributed to several factors. For one, genetic mutations can lead to irregularities in the synthesis of endocannabinoids or their receptors. Additionally, chronic stress can deplete levels of these essential compounds over time.
Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in omega-3 fatty acids, may also contribute to a disrupted endocannabinoid balance. Lastly, environmental factors such as exposure to toxins or prolonged inflammation can hinder endocannabinoid production and effectiveness.
There are many ways you can get endocannabinoids naturally. Some of the best ones include:
- Regular exercise
- Eating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids
- Eating dark chocolate
- Getting adequate sleep
- Meditating