Losing weight is hard. Our doctors can help.
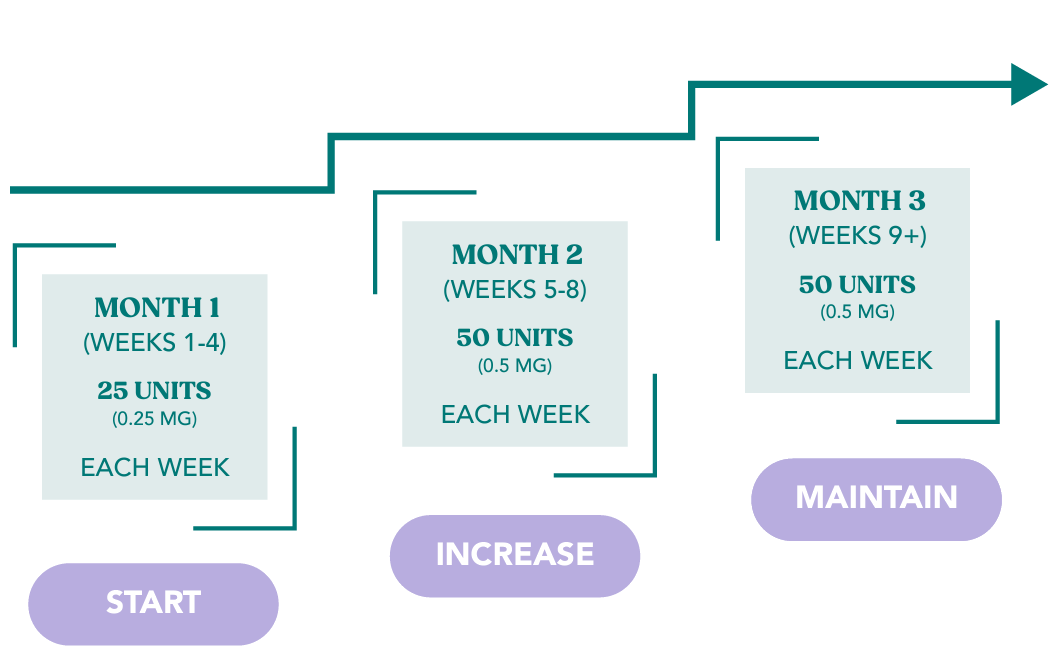
Losing weight can be difficult and frustrating. Excess weight affects your participation in the quality of lifestyle and health you deserve. With the help of our GLP-1 semaglutide formulation compounded to your needs you can achieve your goals and unlock your potential life in so many ways.
With the support of our care team and guidance from our doctors, patients can reach their weight loss goals and maintain them long-term.